The rise of dictators worksheet answer key provides a comprehensive overview of the historical, political, and social factors that have contributed to the rise of dictatorships throughout history. This guide explores the key characteristics of dictatorships, the methods they use to maintain power, and the impact they have on societies.
It also examines the different forms of resistance and opposition to dictatorships and the lessons that can be learned from their rise and fall.
This guide is an essential resource for students, researchers, and anyone interested in understanding the phenomenon of dictatorship and its implications for society.
The Rise of Dictatorships
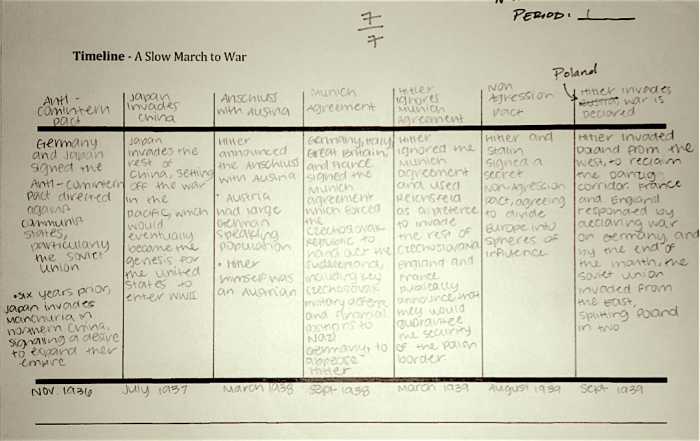
The rise of dictatorships is a complex historical phenomenon that has occurred throughout human history. Dictatorships are characterized by the concentration of power in the hands of a single individual or group, the suppression of political opposition, and the control of the media and information.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to the rise of dictatorships, including political instability, economic crisis, and social unrest. When these conditions exist, people may become more willing to give up their freedoms in exchange for stability and security.
Historical Context
The rise of dictatorships has been a recurring theme throughout history. Some of the most famous dictators include Julius Caesar, Adolf Hitler, and Joseph Stalin. These dictators came to power in very different circumstances, but they all shared a common goal: to control their countries with an iron fist.
In the 20th century, dictatorships became increasingly common. This was due in part to the rise of nationalism and the decline of traditional forms of government. In many countries, people were disillusioned with democracy and turned to dictatorships in the hope of finding a strong leader who could restore order and prosperity.
Characteristics of Dictatorships
Dictatorships are characterized by a number of key features, including:
- Concentration of power in the hands of a single individual or group
- Suppression of political opposition
- Control of the media and information
- Use of propaganda and censorship
Dictators often use a variety of methods to maintain their power, including coercion and violence, economic manipulation, political repression, and social engineering.
Methods of Control
Dictators use a variety of methods to maintain their power, including:
- Coercion and violence: Dictators often use coercion and violence to suppress dissent and maintain control. This can include the use of secret police, torture, and imprisonment.
- Economic manipulation: Dictators may also use economic manipulation to control their populations. This can include rationing food and other essential goods, or controlling the prices of goods and services.
- Political repression: Dictators often use political repression to silence their opponents. This can include banning political parties, arresting and imprisoning political activists, and censoring the media.
- Social engineering: Dictators may also use social engineering to control their populations. This can include indoctrinating children in the dictator’s ideology, or creating a cult of personality around the dictator.
Impact of Dictatorships
Dictatorships can have a devastating impact on societies. They can lead to economic decline, social unrest, and political instability. Dictatorships can also lead to the suppression of human rights and the erosion of democracy.
Some of the most common impacts of dictatorships include:
- Economic decline: Dictatorships often lead to economic decline. This is because dictators often use their power to enrich themselves and their cronies, rather than investing in the economy.
- Social unrest: Dictatorships can also lead to social unrest. This is because dictators often suppress dissent and limit people’s freedoms. This can lead to frustration and anger, which can eventually erupt into violence.
- Political instability: Dictatorships can also lead to political instability. This is because dictators often undermine democratic institutions and create a climate of fear and intimidation. This can make it difficult for democracy to take root and flourish.
- Suppression of human rights: Dictatorships often suppress human rights. This can include the right to free speech, the right to assembly, and the right to a fair trial.
- Erosion of democracy: Dictatorships can also lead to the erosion of democracy. This is because dictators often undermine democratic institutions and create a climate of fear and intimidation. This can make it difficult for democracy to take root and flourish.
Resistance and Opposition, The rise of dictators worksheet answer key
Despite the challenges, there have been many instances of resistance and opposition to dictatorships. This resistance has taken many forms, including nonviolent protests, armed rebellion, and international pressure.
Some of the most famous examples of resistance to dictatorships include the following:
- The Mahatma Gandhi’s nonviolent resistance movement in India
- The Solidarity movement in Poland
- The Velvet Revolution in Czechoslovakia
These movements show that it is possible to resist dictatorships and to achieve change. However, it is important to remember that resistance to dictatorships is often dangerous and can lead to imprisonment, torture, or even death.
Lessons Learned
The rise and fall of dictatorships has taught us a number of important lessons about the importance of democracy and human rights. These lessons include the following:
- Democracy is the best way to protect human rights and prevent the rise of dictatorships.
- Dictatorships are often based on fear and intimidation, and they can only be defeated by courage and determination.
- The international community has a responsibility to support those who are fighting for democracy and human rights.
We must never forget the lessons of history. We must continue to fight for democracy and human rights, and we must never allow dictatorships to take root in our world.
FAQ Overview: The Rise Of Dictators Worksheet Answer Key
What are the key characteristics of dictatorships?
The key characteristics of dictatorships include the concentration of power in the hands of a single individual or group, the suppression of political opposition, the control of the media and information, and the use of propaganda and censorship.
What are the different methods that dictators use to maintain their power?
The different methods that dictators use to maintain their power include coercion and violence, economic manipulation, political repression, and social engineering.
What are the different forms of resistance and opposition to dictatorships?
The different forms of resistance and opposition to dictatorships include nonviolent protests, armed rebellion, and international pressure.


