Which of the following statements about phylogenetic trees is true? This intriguing question opens a gateway into the fascinating world of evolutionary biology, where phylogenetic trees serve as indispensable tools for deciphering the intricate tapestry of life’s history.
Phylogenetic trees, visual representations of evolutionary relationships among species, provide a wealth of information about the shared ancestry and divergence patterns of organisms. They enable scientists to trace the evolutionary trajectory of species, inferring their common ancestors and the branching events that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth.
Phylogenetic Tree Definition and Overview
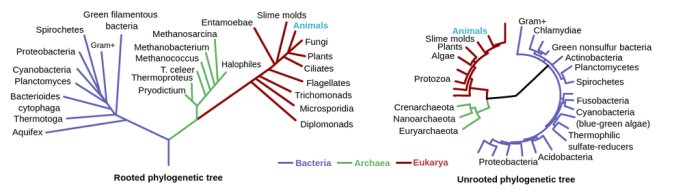
Phylogenetic trees are diagrammatic representations of evolutionary relationships among different species or other taxa. They depict the branching patterns that connect ancestors and descendants over time, providing a visual representation of the evolutionary history of a group of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees play a crucial role in evolutionary biology by providing a framework for understanding the diversification of life on Earth. They allow researchers to infer evolutionary relationships, trace the origins of species, and study the processes that have shaped the evolution of different lineages.
Types of Phylogenetic Trees
- Rooted trees:Have a designated root that represents the common ancestor of all taxa in the tree.
- Unrooted trees:Do not have a designated root, indicating that the root is unknown or not relevant to the analysis.
- Cladistic trees:Focus on shared derived characters (synapomorphies) to define groups of related taxa (clades).
- Phenetic trees:Based on overall similarity or distance measures between taxa, without considering shared ancestry.
Methods for Constructing Phylogenetic Trees
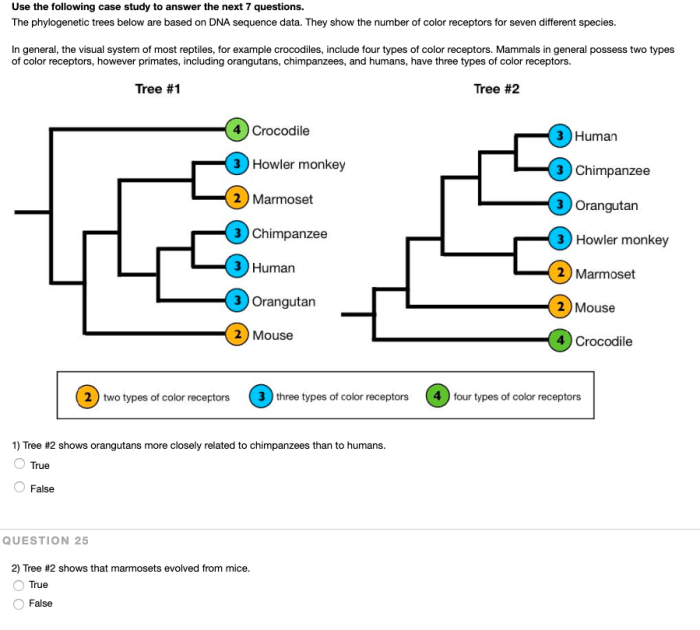
There are various methods used to construct phylogenetic trees, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Distance-based methods:
- Neighbor-joining:A widely used method that calculates the distance between pairs of taxa and iteratively builds a tree.
- UPGMA (Unweighted Pair-Group Method with Arithmetic Mean):A simple and intuitive method that groups taxa based on average distances.
Character-based methods:
- Maximum parsimony:Finds the tree that requires the fewest evolutionary changes (mutations or character state changes) to explain the observed data.
- Maximum likelihood:Estimates the tree that is most likely to have produced the observed data, based on a statistical model of evolution.
- Bayesian inference:Uses statistical methods to calculate the probability of different tree topologies, given the observed data.
Molecular data in phylogenetic tree construction:
Molecular data, such as DNA sequences, play a significant role in phylogenetic tree construction. Molecular data provides genetic information that can be used to identify similarities and differences between species, allowing researchers to infer evolutionary relationships.
Interpreting Phylogenetic Trees
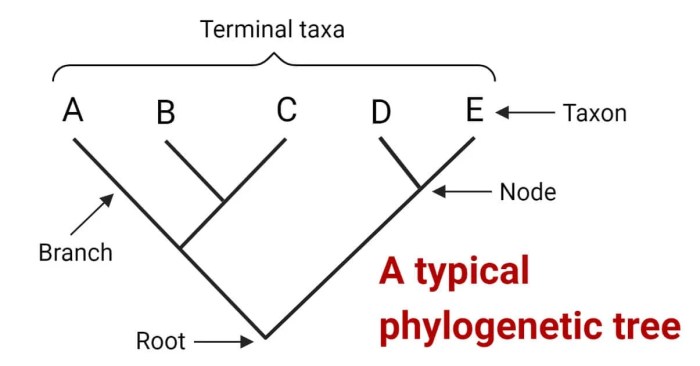
Phylogenetic trees can be interpreted to gain insights into evolutionary relationships and patterns.
Reading and interpreting phylogenetic trees:
- Branch lengths:Represent the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along a branch.
- Nodes:Points where branches split or connect, representing common ancestors or descendants.
- Taxa:Species or other taxa represented by the tips of the tree.
Types of information obtained from phylogenetic trees:
- Evolutionary relationships:The branching patterns show the inferred relationships between different species or taxa.
- Common ancestors:Nodes represent common ancestors, providing insights into the origins of different groups.
- Rates of evolution:Branch lengths can indicate the relative rates of evolutionary change in different lineages.
- Ancestral character states:Phylogenetic trees can be used to infer the character states of ancestral species.
Inferring evolutionary relationships:
Phylogenetic trees provide a framework for inferring evolutionary relationships by tracing the branching patterns and identifying shared ancestors and descendants.
Limitations of Phylogenetic Trees
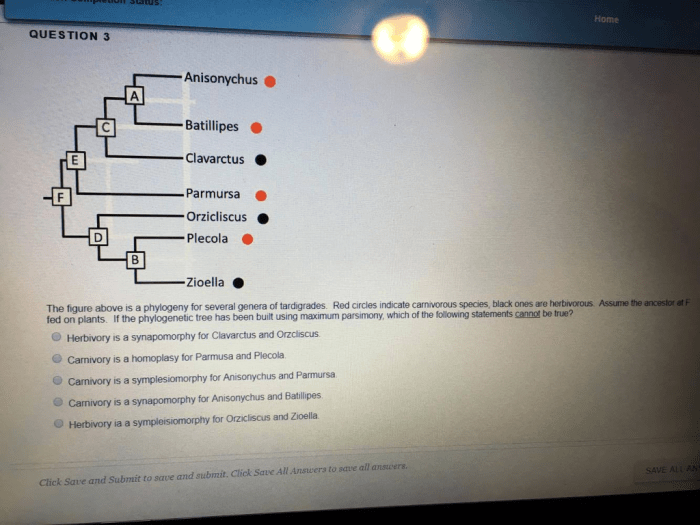
Phylogenetic trees have limitations that can affect their accuracy and reliability.
Factors affecting accuracy:
- Incomplete data:Missing or incomplete data can lead to uncertainties in tree construction.
- Homoplasy:Shared characters that are not due to common ancestry can mislead tree-building algorithms.
- Model assumptions:Phylogenetic tree construction methods rely on assumptions about the evolutionary process, which may not always be accurate.
Evaluating reliability:, Which of the following statements about phylogenetic trees is true
- Bootstrapping:Resampling the data to assess the support for different branches of the tree.
- Bayesian posterior probabilities:Calculating the probability of different tree topologies, given the data.
Applications of Phylogenetic Trees: Which Of The Following Statements About Phylogenetic Trees Is True
Phylogenetic trees are widely used in various fields, including:
Biodiversity studies:
- Identifying and classifying species:Phylogenetic trees help researchers identify and classify new species by comparing them to known species.
- Understanding evolutionary patterns:Trees provide insights into the evolutionary relationships and diversification patterns of different groups of organisms.
Evolutionary history:
- Tracing the origins of species:Phylogenetic trees allow researchers to trace the evolutionary history of species and identify their ancestral origins.
- Studying adaptive radiation:Trees can reveal how species have diversified and adapted to different environments.
Medical research:
- Comparative genomics:Phylogenetic trees are used to compare the genomes of different species, providing insights into gene function and evolution.
- Disease transmission:Trees can help identify the evolutionary relationships between pathogens and their hosts, aiding in understanding disease transmission.
Detailed FAQs
What is the primary function of a phylogenetic tree?
Phylogenetic trees depict the evolutionary relationships among species, providing insights into their shared ancestry and divergence patterns.
How are phylogenetic trees constructed?
Phylogenetic trees can be constructed using various methods, including comparative anatomy, molecular data analysis, and fossil records.
What information can be inferred from phylogenetic trees?
Phylogenetic trees provide information about common ancestors, evolutionary divergence times, and the branching patterns that have shaped the diversity of life.