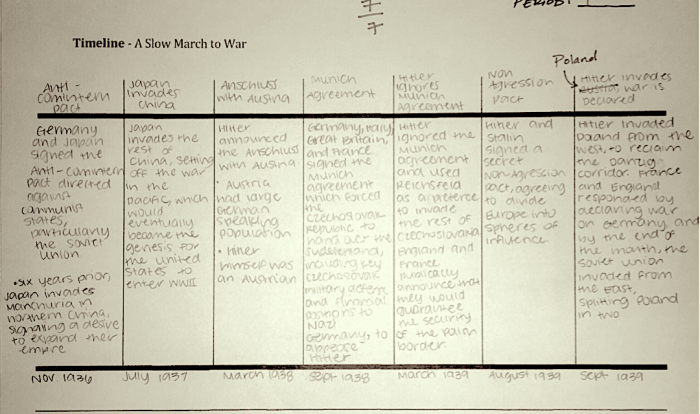
How did the rise of dictators lead to ww2 – Delving into how the rise of dictators precipitated the outbreak of World War II, this analysis unravels a complex narrative of political turmoil, economic instability, and the erosion of international cooperation. The rise of dictatorships in the interwar period created a tinderbox of tensions that ultimately ignited the flames of global conflict.
Dictators such as Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, and Joseph Stalin emerged as charismatic but ruthless leaders, exploiting economic crises and political instability to seize power. Their aggressive foreign policies, territorial ambitions, and disregard for international norms shattered the fragile peace established after World War I.
Rise of Dictatorships in the Interwar Period

The rise of dictatorships in Europe following World War I was a complex phenomenon driven by a confluence of factors, including economic instability, political polarization, and the rise of nationalist movements. These factors created a fertile ground for the emergence of charismatic leaders who promised stability, order, and a return to national greatness.
Economic Instability
The economic turmoil of the post-war period, including high inflation, unemployment, and social unrest, weakened democratic governments and made them vulnerable to authoritarian alternatives. Dictators exploited these economic hardships to gain popular support by promising to restore economic prosperity and stability.
Political Polarization
The war had deeply divided European societies along ideological lines, with communists, socialists, and conservatives vying for power. This political polarization made it difficult for democratic governments to build consensus and implement effective policies, creating a vacuum that dictators filled.
Nationalism, How did the rise of dictators lead to ww2
The war had also stoked nationalist sentiments, which dictators manipulated to gain support. They promised to restore national pride, reclaim lost territories, and protect the nation from external threats, appealing to a sense of national unity and superiority.
Prominent Dictators and Their Ideologies
Among the most prominent dictators who rose to power during this period were:
- Adolf Hitler (Nazi Germany):Nationalist, anti-Semitic, and fascist
- Benito Mussolini (Fascist Italy):Nationalist, authoritarian, and anti-communist
- Joseph Stalin (Soviet Union):Communist, totalitarian, and dictator
Questions and Answers: How Did The Rise Of Dictators Lead To Ww2
How did economic instability contribute to the rise of dictatorships?
Economic crises created widespread unemployment, poverty, and social unrest, which fueled support for authoritarian leaders who promised stability and economic recovery.
What was the impact of nationalism on the rise of dictatorships?
Nationalism played a significant role by creating a sense of national pride and grievance, which dictators exploited to gain popular support and justify aggressive foreign policies.
How did dictators consolidate their power?
Dictators employed various tactics to consolidate their power, including propaganda, censorship, suppression of dissent, and the establishment of secret police forces.