Consider the following waves representing electromagnetic radiation. – Consider the following waves representing electromagnetic radiation: a symphony of energy that permeates our universe. From the gentle hum of radio waves to the penetrating power of gamma rays, electromagnetic waves encompass a vast spectrum, each with unique characteristics and applications.
This discourse will delve into the nature of electromagnetic radiation, exploring the different types of waves based on their wavelength and frequency. We will examine their fundamental properties, including speed, energy, and polarization, and discuss how these properties influence their interactions with matter.
1. Introduction
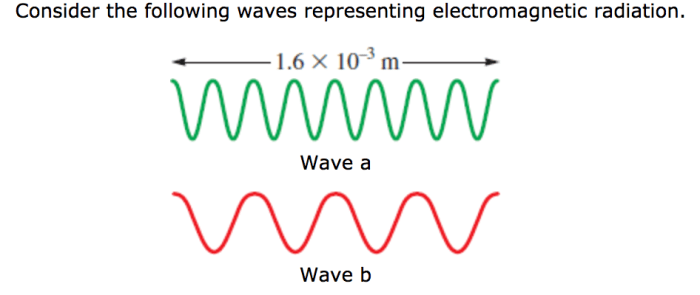
Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a form of energy that travels through space in the form of waves. EMR waves are characterized by their wavelength and frequency, which determine their energy and properties. EMR waves encompass a wide range of wavelengths, from short gamma rays to long radio waves, forming the electromagnetic spectrum.
EMR waves are produced by the acceleration of charged particles, such as electrons. When an electron is accelerated, it emits an EMR wave with a wavelength that is inversely proportional to the acceleration. The frequency of the EMR wave is directly proportional to the energy of the electron.
2. Types of Electromagnetic Radiation Waves
EMR waves are classified into different types based on their wavelength and frequency. The electromagnetic spectrum categorizes EMR waves into seven main types, from longest to shortest wavelength: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Radio waveshave the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies. They are used for communication, navigation, and remote sensing.
- Microwaveshave shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. They are used for cooking, communication, and radar.
- Infrared radiationhas even shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than microwaves. It is used for heating, night vision, and remote sensing.
- Visible lightis the only type of EMR wave that can be detected by the human eye. It has a wavelength range of 400 to 700 nanometers.
- Ultraviolet radiationhas shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than visible light. It is used for tanning, disinfection, and phototherapy.
- X-rayshave even shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than ultraviolet radiation. They are used for medical imaging and security screening.
- Gamma rayshave the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies. They are produced by radioactive decay and are used for cancer treatment and medical imaging.
3. Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Waves

EMR waves have several fundamental properties, including speed, energy, and polarization.
- Speed: EMR waves travel at the speed of light, which is approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second.
- Energy: The energy of an EMR wave is directly proportional to its frequency. Gamma rays have the highest energy, while radio waves have the lowest energy.
- Polarization: EMR waves can be polarized, which means that their electric fields oscillate in a specific direction. Polarization is used in a variety of applications, such as sunglasses and 3D movies.
The properties of EMR waves determine how they interact with matter. For example, gamma rays have high energy and can penetrate matter easily, while radio waves have low energy and are easily absorbed by matter.
4. Applications of Electromagnetic Radiation Waves
EMR waves have a wide range of applications across various fields.
- Communication: EMR waves are used for communication purposes, such as radio, television, and mobile phones.
- Medicine: EMR waves are used for medical imaging, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. They are also used for cancer treatment, such as radiation therapy.
- Industry: EMR waves are used in a variety of industrial applications, such as welding, cutting, and heating.
- Research: EMR waves are used in research to study the structure and properties of matter. They are also used to study the universe, such as through radio astronomy and gamma-ray astronomy.
As technology advances, new applications for EMR waves are constantly being developed.
Frequently Asked Questions: Consider The Following Waves Representing Electromagnetic Radiation.
What is the nature of electromagnetic radiation?
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that consists of electric and magnetic fields oscillating in phase, propagating through space as waves.
How are electromagnetic waves classified?
Electromagnetic waves are classified based on their wavelength and frequency, which determine their energy and applications.
What are the key properties of electromagnetic waves?
The key properties of electromagnetic waves include speed (constant in a vacuum), energy (proportional to frequency), and polarization (orientation of electric field).